Spring Batch Karp Rabin
Pattern Matching
for DNA Sequencing Data
Using Spring Batch
and Karp Rabin
Author : Wadï
Mami
E-mail : wmami@steg.com.tn/ didipostman77@gmail.com
Date : 17/06/2012
Abstract :
Processing large volume of
data has always been a major problem due to the increasing volume of the
data. Batch processing can be applied in
many use cases. Among them why not Pattern Matching for DNA Sequencing Data. In this article, I am going to demonstrate
batch processing using one of the projects of Spring which is Spring Batch. Spring Batch
provides functions for processing large volumes of data in batch jobs. In our
case reading DNA file or database table and seeking for patterns I mean all the locations of the specified pattern inside a DNA sequence.
Spring batch to process
huge data :
Spring Batch is a lightweight,
comprehensive batch framework designed to
enable the development of
robust batch applications vital for the daily
operations of enterprise
systems.
Spring Batch reads and process DNA sequentially until reaching commit-interval value then it writes transformed items (DNA) simultaneously.
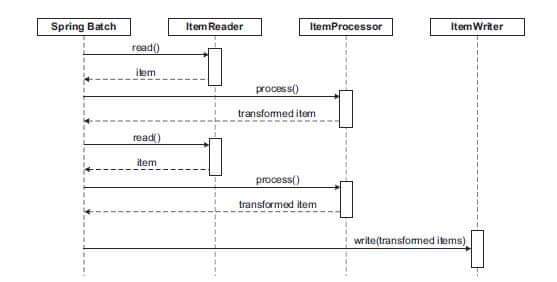
Spring Batch uses a 'Chunk Oriented'
processing style within its most common
implementation. Chunk oriented processing refers
to reading the data one at a
time, and creating 'chunks' that will be
written out, within a transaction
boundary. One item is read in from an ItemReader, handed to
an ItemProcessor, and aggregated. Once the number of items
read equals the
commit interval.
, the entire chunk is written out via
the ItemWriter, and then the transaction is
committed.
Below is a code representation of the same concepts
shown above:
List items = new
Arraylist();
for(int i = 0; i < commitInterval;
i++){
Object item = itemReader.read()
Object processedItem =
itemProcessor.process(item);
items.add(processedItem);
}
itemWriter.write(items);
A step is an object that
encapsulates a sequential phase of a job and holds all the
necessary information to
define and control processing. It delegates all the
information
to a Job (job.xml) to carry out its
task.
|
<job id="dnaSeq"> |
|
|
<step id="dnaSeqStep"> |
|
|
<tasklet transaction-manager="transactionManager"> |
|
|
<chunk reader="csvItemReader" writer="csvItemWriter" |
|
|
processor="DNA_SequenceProcessor" commit-interval="2"> |
|
|
</chunk> |
|
|
</tasklet> |
|
|
</step> |
|
|
</job> |
Configuring ItemReader
We will now define ItemReader for
our model which will be used for
reading data from CSV file.
<bean:bean
id="csvItemReader"
class="org.springframework.batch.item.file.FlatFileItemReader"
scope="step">
<bean:property name="resource"
value="classpath:ch02/data/DNA.csv"/>
<bean:property
name="lineMapper">
<bean:bean
class="org.springframework.batch.item.file.mapping.DefaultLineMapper">
<bean:property name="lineTokenizer"
ref="lineTokenizer"/>
<bean:property
name="fieldSetMapper">
<bean:bean
class="org.springframework.batch.item.file.mapping.BeanWrapperFieldSetMapper">
<bean:property
name="prototypeBeanName" value="DNA_Sequence">
</bean:property>
</bean:bean>
</bean:property>
</bean:bean>
</bean:property>
</bean:bean>
<!-- lineTokenizer -->
<bean:bean id="lineTokenizer"
class="org.springframework.batch.item.file.transform.DelimitedLineTokenizer">
<bean:property
name="delimiter" value=","/>
<bean:property
name="names">
<bean:list>
<bean:value>dna</bean:value>
<bean:value>crissprArrays</bean:value>
</bean:list>
</bean:property>
</bean:bean>
Configuring ItemProcessor
<bean:bean id="DNA_SequenceProcessor" scope="step"
class="com.juxtapose.example.ch02.DNA_SequenceProcessor">
</bean:bean>
As you can see I use a DNASequence_Processor class that
implements itemProcessor and use Karp Rabin Algorithm.
ItemWriter
Once the data is processed, the data needs to be stored in a
file as per our requirement.
<bean:bean
id="csvItemWriter"
class="org.springframework.batch.item.file.FlatFileItemWriter"
scope="step">
<bean:property
name="resource" value="file:target/ch02/outputFile.csv"/>
<bean:property name="lineAggregator">
<bean:bean
class="org.springframework.batch.item.file.transform.DelimitedLineAggregator">
<bean:property
name="delimiter" value="|"></bean:property>
<bean:property
name="fieldExtractor">
<bean:bean
class="org.springframework.batch.item.file.transform.BeanWrapperFieldExtractor">
<bean:property
name="names"
value="dna, seqDNA_Arrays">
</bean:property>
</bean:bean>
</bean:property>
</bean:bean>
</bean:property>
</bean:bean>
Conclusion
This article just scratched the surface of Spring Batch in
general. The example used in this article is not production-ready code. You can
define job configuration depending on your project requirements.
Here The Github repository for the project
https://github.com/didipostman/SBKarpRabin

The Ultimate definitive guide on how Spring batch could may explain how CRISPR Cas9Works read this link https://didipostmanprojects.blogspot.com/2023/01/the-definitive-explanation-on-how.html
ReplyDelete